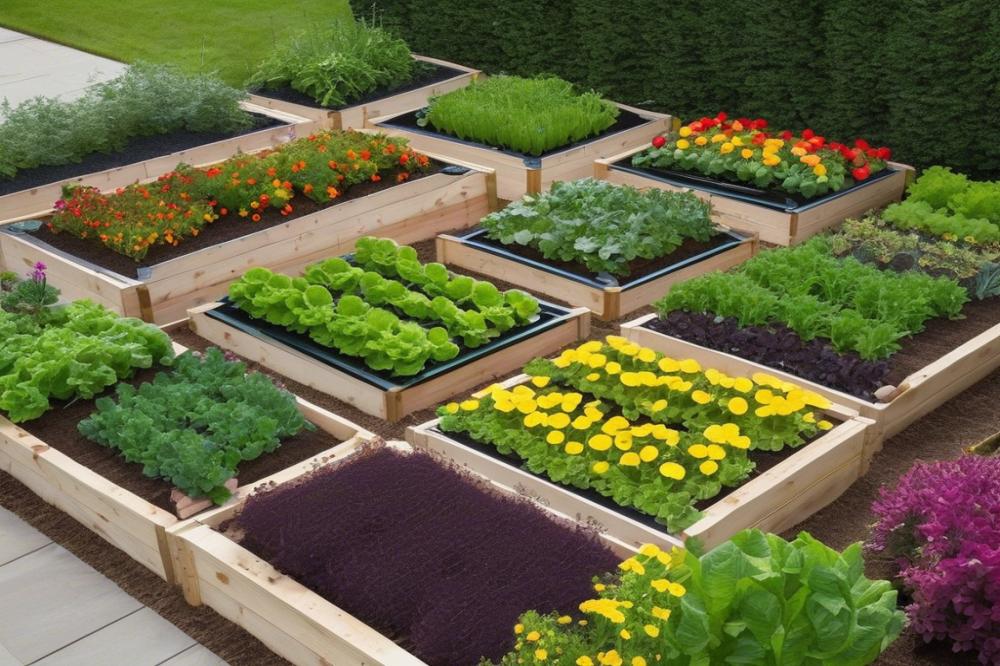
Introduction to crop rotation in raised beds
vegetable gardening benefits greatly from a strategy known as crop rotation. This technique involves changing the types of plants grown in specific areas from season to season. The practice plays a vital role in maintaining soil health. When gardeners rotate their crops, they help prevent soil depletion by ensuring that different plants contribute and consume varying amounts of nutrients.
Healthy soil is crucial for any garden’s success. Rotating crops encourages a diverse range of plants and their root systems. This diversity improves nutrient management by allowing different plants to thrive. For example, legumes can fix nitrogen in the soil, enriching it for future crops that may need it. Engaging in this practice also aids in pest control. Many pests are attracted to specific plant families. Changing the plants in any given area can disrupt their life cycles, reducing infestations.
Sustainable agriculture relies on techniques that conserve resources and promote health. Crop diversity not only boosts soil health but also increases resilience against diseases and pests. Organic gardening often emphasizes this strategy as a way to nurture the ecosystem of the garden.
raised beds provide an ideal environment for implementing crop rotation. These structures allow for better drainage and soil aeration, making it easier for each variety of plant to flourish. Garden planning becomes more effective with raised beds, as each section can be tailored to accommodate the needs of different crops. Seasonal planting becomes a simple task when there’s a clear understanding of what to grow where and when.
Understanding crop rotation empowers gardeners to improve their practices. As you embark on this journey, remember that every choice contributes to a healthier, more productive garden.
Understanding Crop Rotation
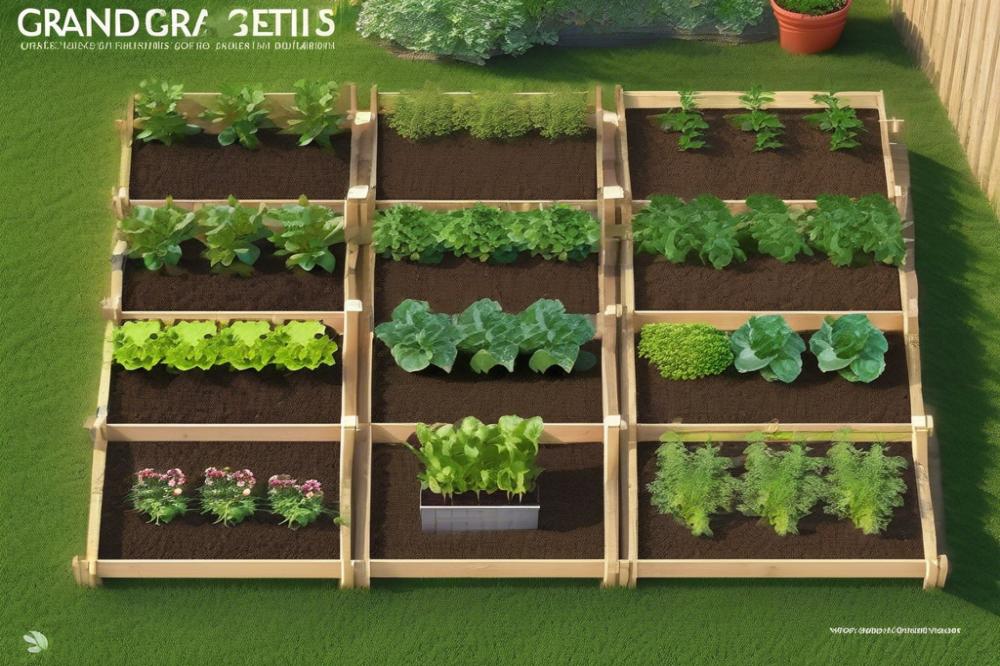


Crop rotation is a farming practice where different types of crops are grown in the same area across seasons. This approach dates back centuries. Ancient civilizations used it to maintain soil health and improve yields. Farmers discovered that switching crops each season helped prevent soil depletion. They noticed that certain plants had different nutrient needs, which allowed the soil to recover.
Basic principles guide this practice. The main goal is to promote soil health and control pests. By planting different crops, farmers reduce the risk of disease and pests. Each plant family has unique characteristics. Some might enrich the soil while others could deplete it. Crop diversity helps break the cycle of pests and diseases that often affect specific plants.
Nutrient management plays a significant role in effective gardening. Different plants extract varying nutrients from the soil. For example, legumes, such as beans, can fix nitrogen in the ground. This ability makes them valuable in a rotation plan. Seasonal planting also aligns with these principles. Understanding when to plant each crop ensures they thrive at the right time.
Integrating variety into garden planning enhances the resilience of crops. Organic gardening often benefits from these techniques as well. Using a mix of vegetables not only promotes a better yield but can also improve flavor. Crop rotation is a critical practice in sustainable agriculture. It allows for a more balanced ecosystem within a garden, proving that nature thrives on diversity.
Planning Your Raised Bed Garden for Crop Rotation

Creating a successful raised bed garden involves careful planning. You must think about the variety of vegetables you wish to grow. Grouping plants by their families helps in organizing your garden efficiently. For instance, tomatoes and peppers belong to the nightshade family. This method aids in monitoring soil health and understanding nutrient requirements.
Consider rotating crops among different beds each season. This practice prevents pest control problems and reduces diseases that can be soil-borne. Rotating families, such as legumes or brassicas, can rejuvenate the soil. Legumes, like beans and peas, enrich the soil with nitrogen. Brassicas include cabbage, broccoli, and kale. They tend to use different nutrients from the soil, which balances nutrient management.
Plan your garden layout with seasonal planting in mind. Start with cool-season crops in early spring. As temperatures rise, transition to heat-tolerant varieties later in the season. Utilizing crop diversity allows for more resilience in your garden. This aspect of organic gardening encourages biodiversity, which can be beneficial for pest management.
Keep track of what was planted each season. A simple log can help you remember, making garden planning smoother for the next year. Mark out each bed and color-code based on plant families. This strategy will make crop rotation much simpler and more organized.
Evaluate the needs of different plants. Some vegetables thrive in full sun, while others prefer partial shade. Understanding these light preferences can enhance growth. By optimizing your raised beds for these conditions, you can enjoy a more fruitful harvest. Planning also entails being aware of companion planting. Some plants naturally deter pests, while others can inhibit growth.
In summary, thoughtful preparation is essential in raised bed gardening. With a solid foundation, your soil health can improve year after year. Seasonal planting promotes a thriving ecosystem, supporting sustainable agriculture practices. Pay attention to the relationships between different plant families for better results. Each step you take in garden planning can yield significant benefits.
Implementing Crop Rotation in Raised Beds


Getting started with crop rotation in raised beds involves careful planning. First, identify the vegetable varieties you want to plant. Consider grouping them by plant families. For example, tomatoes, peppers, and eggplants belong to the same nightshade family and should not follow each other in planting.
Next, create a planting schedule that reflects seasonal planting. This schedule will help you understand when to sow seeds and when to harvest. For cool-season crops like lettuce and spinach, April may be an ideal time to plant. Warm-season vegetables like zucchini and corn generally do better if planted in late May or early June.
Determining the right timing for planting and harvesting is crucial for maintaining soil health. Each vegetable requires specific nutrients during its growth cycle. Rotating crops every year will help balance nutrient management and prevent soil depletion.
Here’s a simple example of crop rotation. In the first year, plant leafy greens such as spinach. In the following year, sow legumes like beans or peas. These plants add nitrogen to the soil, enriching it. Afterward, consider planting root vegetables like carrots or beets. By the third year, plant fruiting crops like tomatoes or peppers. This method promotes crop diversity, enhancing the overall health of your garden.
Take note of pests that may affect your raised bed garden. Different families of plants often attract distinct pests. For instance, if aphids target a particular crop, avoid planting that crop in the same spot the next year. Rotate the affected plants to a new location to help with pest control.
When planning your garden, use a visual map of your raised beds. Mark which crops are planted in each area. This record will be a useful reminder for rotation in subsequent years. Organic gardening practices benefit significantly from consistent crop rotation.
Maintaining a diverse selection of plants maximizes your gardening success. Raised beds offer the flexibility to experiment with various crops. Incorporating this rotation technique will lead to a healthier ecosystem in your garden space. Over time, these changes contribute to sustainable agriculture and productive vegetable gardening.
Maintaining Soil Health and Pest Control through Crop Rotation


Crop rotation plays a crucial role in maintaining soil health in raised beds. Different plants have unique nutrient requirements and contribute differently to the soil. When you grow the same crop in one spot year after year, certain nutrients can get depleted. Specific plants may also leave behind residues that could attract pests or diseases. By alternating your crops, you can avoid these problems and promote a more balanced soil ecosystem.
Healthy soil is vital for successful vegetable gardening. Each plant family has its own way of interacting with soil. For example, legumes can fix nitrogen, adding this nutrient back into the ground. Rotating these plants with heavy feeders like tomatoes or peppers allows for improved nutrient management throughout the growing season. The effects on soil structure can be significant, too. A variety of root systems can aerate the soil and improve drainage, making it more resilient.
Pest control is another benefit to diverse planting. Many pests and diseases prefer specific plants. By changing what you plant, you can disrupt their life cycles. This limits their ability to thrive and spread. Additionally, some crops naturally deter pests. Marigolds and nasturtiums, for instance, can repel aphids and other unwanted insects. Integrating these plants into your seasonal planting calendar enhances biodiversity and provides natural pest relief.
Enhancing soil fertility can also be part of your plan. Alongside rotation, consider adding organic matter like compost or well-rotted manure. These amendments enrich the soil and supply essential nutrients for healthy plant growth. Cover crops can also be a valuable strategy. Growing crops like clover or rye during the off-season can improve soil structure and nutrient levels once turned under.
Proper garden planning involves understanding plant families and their relationships. Some families are more compatible with each other than others. Moving plants around helps prevent nutrient depletion and keeps pests at bay. For instance, following squash with leafy greens can have beneficial effects on growth.
Practices that incorporate sustainable agriculture principles not only support soil health but promote a healthy gardening ecosystem overall. Crop diversity fosters resilience, making your raised beds less susceptible to failing crops. Each action in your garden matters, and with careful thought, you can create a dynamic space that thrives more every season.
Challenges and Solutions in Crop Rotation
Gardeners often encounter several challenges when rotating crops in raised beds. One major issue is space limitations. Raised beds can restrict the number of plants that one can grow in a given area. To tackle this problem, consider using vertical gardening techniques or companion planting. These methods can maximize space and allow for a more productive garden.
Soil health can also be a concern. Continuously planting the same type of crops can deplete nutrients over time. Implementing a plan that involves regular soil testing can help determine nutrient levels. Adding compost or organic fertilizers ensures that the soil remains rich and vibrant. Diversifying the vegetables grown will contribute to nutrient management and improve overall quality.
Pest control is another common challenge faced by gardeners. Some pests can become more prevalent if the same plant families are grown in the same spots year after year. Changing plant types each season can disrupt the life cycles of these pests. Introducing beneficial insects or planting pest-repelling herbs are effective strategies. Integrated pest management is a practical aspect to consider.
Seasonal considerations can complicate planning. Certain plants thrive in specific climates and might not be available for every growing season. To counter this, it’s wise to keep a journal or garden planner. This way, one can track what was planted in previous years and adjust accordingly. Flexibility is key in making the most of seasonal variations.
Lastly, some may struggle to understand the different plant families and their unique needs. Not every vegetable has the same soil requirements or susceptibility to pests. Resources such as gardening guides or local extension services can be invaluable. They help define which plants belong together in a rotation scheme.
Each of these challenges requires thoughtful solutions. Emphasizing adaptability in your garden planning is crucial. Consider experimenting with various strategies as you manage your raised beds. The more you learn through experience, the more successful your vegetable gardening efforts will become. Sustainable agriculture depends on this commitment to crop diversity and environmental stewardship.
Embracing the Benefits of Smart Planting
In summary, rotating crops in raised beds plays a vital role in successful gardening. Understanding how different plants affect one another can help improve your harvest. Vegetables thrive when grown in a diverse environment, which is often overlooked.
Soil health is significantly enhanced by this practice, as it helps maintain nutrient balance. Different plants have varying nutrient needs. By alternating crops, you prevent the depletion of essential elements from the soil. This promotes a richer and more productive growing medium.
Another key advantage lies in pest control. Certain crops naturally deter pests that affect others. By changing the location of these plants each season, you can disrupt pest life cycles. This reduces the chances of infestations without heavy reliance on chemicals.
Practicing this method also contributes to sustainable agriculture. Building resilience in your garden benefits not only you but the ecosystem as a whole. Many small steps lead to healthier farming, and species diversity is one of the most impactful.
Take a moment to consider the benefits outlined here. Implementing rotation techniques can elevate your vegetable gardening success. Start planning your garden layout today with these ideas in mind, and enjoy the journey towards better gardening results.



